Cybersecurity Threats Malware Viruses and Other Online Dangers
페이지 정보
작성자 Kaley 댓글 0건 조회 5회 작성일 24-10-23 17:03본문

In the intricate web of the digital age, the protection of sensitive data has become paramount. This section delves into the various strategies and challenges associated with maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of electronic information. As our reliance on digital platforms grows, so does the necessity for robust measures to shield against potential vulnerabilities.
Understanding the Risks: Every click, download, and online transaction carries a certain level of risk. This includes exposure to malicious software, unauthorized access, and data breaches. It is crucial to comprehend these risks in order to implement effective countermeasures.
Protecting Your Digital Footprint: From phishing attempts to sophisticated hacking techniques, the threats are diverse and ever-evolving. This article explores the landscape of digital security, providing insights into how individuals and organizations can fortify their defenses against these evolving challenges.
Understanding Cybersecurity Threats
In this section, we delve into the escalating issue of malicious software attacks, a critical component of the digital defense landscape. These attacks are not only becoming more frequent but also increasingly sophisticated, posing significant challenges to individuals and organizations alike.
The Rise of Malware Attacks
Malicious software, or malware, has seen a dramatic increase in both prevalence and complexity. This type of software is designed to infiltrate or damage computer systems without the owner's consent. The motives behind these attacks vary, ranging from financial gain to espionage, and even to mere disruption for ideological reasons.
One of the primary reasons for the surge in malware attacks is the ease with which such software can be developed and distributed. With the advent of the dark web and other clandestine online networks, the tools and knowledge required to create malware are more accessible than ever. This accessibility has led to a proliferation of amateur and professional cybercriminals alike, each contributing to the growing threat landscape.
Moreover, the evolution of malware has seen traditional viruses and worms being supplemented by more advanced forms such as ransomware, spyware, and trojans. Each of these variants has unique capabilities and targets, making comprehensive defense strategies increasingly complex. For instance, ransomware encrypts a victim's files and demands payment for their release, while spyware covertly gathers information from an infected system.
The impact of these attacks extends beyond the immediate data loss or system damage. They can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions for businesses. For individuals, the consequences can include identity theft and the loss of sensitive personal data.
To combat this rising threat, it is essential for both individuals and organizations to stay informed about the latest malware trends and to implement robust security measures. This includes regular software updates, the use of antivirus and anti-malware tools, and employee education Find out on Medium safe computing practices.
In conclusion, the escalation of malware attacks is a pressing concern in the digital age. Understanding the nature and evolution of these threats is the first step towards developing effective countermeasures and ensuring the safety and integrity of our digital environments.
The Rise of Malware Attacks
In recent years, the digital landscape has witnessed a significant surge in malicious software attacks. This section delves into the various forms of harmful software that pose risks to systems and data integrity. Understanding these threats is crucial for implementing effective protective measures.
Malicious software, commonly referred to as malware, comes in various types, each designed with different objectives. Below are some of the most prevalent forms:
- Virus: A self-replicating program that attaches itself to a host file, often causing damage to the system as it spreads.
- Worm: Similar to a virus but capable of self-replication without attaching to other files, worms can quickly consume system resources.
- Trojan Horse: Disguised as legitimate software, Trojans deceive users and grant unauthorized access to attackers, often leading to data theft or system corruption.
- Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts user files and demands a ransom for decryption keys, causing significant operational disruptions.
- Spyware: Software that secretly monitors user activity and can transmit sensitive information to unauthorized parties.
- Adware: While not always malicious, adware displays unwanted advertisements and can compromise system performance and user privacy.
Each type of malware requires specific countermeasures. For instance, antivirus software is effective against viruses and some forms of spyware, while firewalls and intrusion detection systems can help mitigate the risks associated with worms and Trojans. Regular updates and patches are also essential to protect against known vulnerabilities exploited by malware.
In conclusion, the rise of malware attacks underscores the importance of proactive defense strategies. By understanding the nature of these threats and implementing robust security protocols, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to these malicious programs.
Exploring Types of Computer Viruses

This section delves into the various forms of malicious software that can infect systems, causing significant disruptions and potential data loss. While the term "virus" is often used broadly to describe any form of harmful code, it is crucial to understand the specific types and their unique characteristics to effectively safeguard digital environments.
| Type | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Boot Sector Viruses | These viruses target the boot sector of a hard drive, which is crucial for the system's startup process. | Can prevent the system from booting, leading to complete system failure. |
| File Infectors | These viruses attach themselves to executable files (.exe or .com) and activate when the file is run. | Can cause system instability and data corruption. |
| Macro Viruses | These are written in macro languages of applications like Microsoft Word or Excel. | Can spread rapidly through documents and cause widespread data corruption. |
| Polymorphic Viruses | These viruses change their code with each infection, making them difficult to detect by signature-based antivirus software. | Can evade detection and persist in systems for long periods. |
| Worms | Unlike traditional viruses, worms can self-replicate without attaching to other programs. | Can consume network bandwidth and lead to system slowdowns or crashes. |
Understanding these different types of viruses is essential for developing robust defense mechanisms. Each type requires specific strategies for detection and removal, highlighting the importance of continuous updates to security protocols and the use of comprehensive antivirus solutions.
Phishing: A Common Online Scam
In this section, we delve into a prevalent form of digital deception known as phishing. This tactic involves fraudulent attempts to acquire sensitive details such as usernames, passwords, and financial information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in electronic communications. Phishing scams are designed to manipulate individuals into revealing personal data, often through seemingly legitimate emails or messages.
Phishing attacks typically follow a pattern that can be broken down into several stages:
- Deceptive Contact: The scam begins with an unsolicited communication, often an email, text message, or instant message, that appears to come from a reputable source.
- Sense of Urgency: The message often creates a sense of urgency or fear to prompt immediate action, such as a threat of account closure or a time-sensitive offer.
- Request for Information: The communication will usually include a request for personal information, often directing the recipient to a fake website that closely mimics the real one.
- Data Harvesting: Once the user enters their details on the fraudulent site, the attackers collect this information for malicious use.
To protect against phishing, it is crucial to recognize the signs of such scams:
- Be wary of unsolicited communications that ask for personal details.
- Check the email address or URL for inconsistencies or suspicious characters.
- Hover over links to see the actual URL before clicking.
- Use security software that can help detect and block phishing attempts.
Educating oneself and staying vigilant are key defenses against falling victim to phishing scams. Always verify the authenticity of requests for personal information and report any suspicious activity to the relevant authorities or the legitimate entity that the scam is impersonating.
The Impact of Data Breaches on Privacy
In this section, we delve into the profound consequences that unauthorized access to sensitive data can have on individual privacy. The focus is on understanding how such incidents not only compromise personal details but also reshape our perceptions and practices regarding digital security.
Data breaches have become a significant concern in the digital age, affecting millions of users globally. These incidents occur when unauthorized individuals gain access to confidential data, often leading to severe repercussions for those whose information has been exposed. The impact can range from financial losses to identity theft, and even psychological distress.
| Type of Impact | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Unauthorized transactions, loss of funds | Credit card fraud, unauthorized bank transfers |
| Identity Theft | Use of personal information to impersonate the victim | Opening new credit lines, obtaining passports |
| Reputational | Damage to personal or professional reputation | Public exposure of sensitive information, loss of trust |
| Psychological | Stress, anxiety, loss of privacy | Fear of future breaches, constant vigilance |
The table above outlines various types of impacts resulting from data breaches. Each type demonstrates the far-reaching effects that such incidents can have on individuals, underscoring the importance of robust security measures to prevent these occurrences.
In conclusion, data breaches pose a significant threat to privacy and security in the digital realm. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect sensitive information and mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized access.
Protecting Personal Information Online
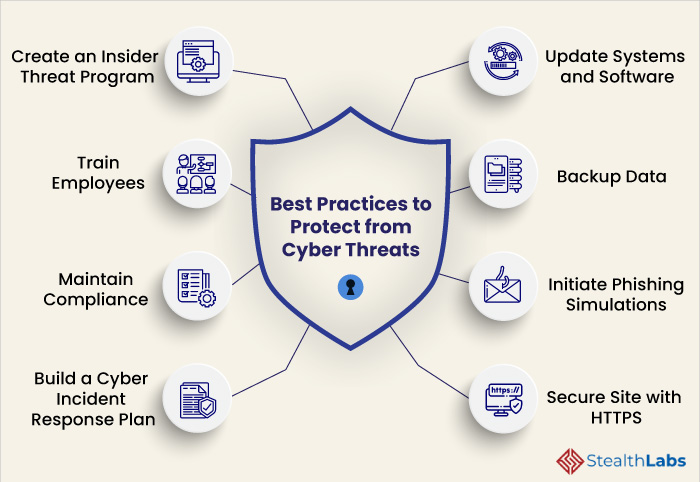
In today's interconnected world, safeguarding sensitive data has become a paramount concern. This section delves into the strategies and practices essential for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of one's digital footprint. It explores how individuals and organizations alike can fortify their defenses against potential breaches, ensuring that critical data remains secure.
Understanding the Risks: Every day, countless individuals interact with various digital platforms, inadvertently exposing their personal details. These can range from basic contact information to more sensitive financial or health records. The vulnerability of such data to unauthorized access or manipulation necessitates a proactive approach to its protection.
The Role of Education: One of the most effective ways to enhance data security is through education. Users must be aware of the common tactics employed by those seeking to exploit personal information. This includes recognizing the signs of fraudulent activities and understanding the importance of strong, unique passwords for different accounts.
Technological Safeguards: Beyond user awareness, technological measures play a crucial role in data protection. Implementing robust encryption methods, using secure networks, and regularly updating software to patch vulnerabilities are essential practices. Additionally, the use of two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access.
Legislation and Compliance: Governments around the world are increasingly enacting laws to protect consumer data. Compliance with these regulations not only ensures legal adherence but also demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding personal information. Organizations must stay informed about these laws and adjust their data handling practices accordingly.
In conclusion, the protection of personal information in the digital realm is a multifaceted challenge that requires a combination of user vigilance, technological solutions, and regulatory compliance. By adopting a comprehensive approach, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with data breaches and ensure the integrity of their digital interactions.
The Role of Cybersecurity in Modern Society
In the contemporary digital landscape, the protection of digital assets and networks has become paramount. This section delves into the critical function of safeguarding electronic systems within our evolving societal framework. As technology advances, so do the complexities and vulnerabilities associated with it, necessitating robust measures to ensure the integrity and security of our digital interactions.
The integration of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various sectors, from healthcare to finance. However, these advancements also introduce new avenues for potential exploitation. For instance, AI systems can be manipulated to misinterpret data or make erroneous decisions, while IoT devices often lack sufficient security protocols, making them easy targets for unauthorized access.
Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and secure nature, also faces challenges. While it provides a high level of security against traditional cyber attacks, new forms of threats, such as 51% attacks and double-spending, can undermine its integrity. Understanding these risks is crucial for developing effective countermeasures and ensuring the technology's continued reliability.
Moreover, the rise of quantum computing poses a significant threat to existing encryption methods. Quantum computers have the potential to crack current encryption algorithms, thereby jeopardizing the security of sensitive data. This necessitates the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms to safeguard against future breaches.
In response to these evolving challenges, strategic approaches to cyber defense must be dynamic and forward-thinking. This includes the implementation of advanced monitoring systems, the adoption of predictive analytics to anticipate threats, and the continuous education of users about safe digital practices. Additionally, collaboration between technology developers, policymakers, and cybersecurity experts is essential to stay ahead of the curve and mitigate emerging risks effectively.
In conclusion, the role of cyber defense in modern society is multifaceted and ever-evolving. It requires a comprehensive understanding of new technologies and their associated vulnerabilities, coupled with proactive and innovative strategies to protect against potential threats. As society continues to embrace technological advancements, the importance of robust cyber defense mechanisms cannot be overstated.
Emerging Technologies and Cyber Risks

As the digital landscape continues to evolve, new technologies bring forth unprecedented opportunities and challenges. This section delves into the complex interplay between cutting-edge advancements and the potential vulnerabilities they introduce, emphasizing the need for robust safeguards against digital exploitation.
Advancements in technology often outpace the development of protective measures, creating a fertile ground for new forms of digital intrusion. Here are some key emerging technologies and the associated risks:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI systems, while enhancing efficiency and decision-making, can be manipulated to mislead or disrupt operations. For instance, deepfake technology can create convincing but false audio or video content, potentially leading to misinformation or fraud.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices in homes and businesses offers convenience but also exposes a vast attack surface. Unsecured devices can be exploited to gain unauthorized access or to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: Although designed to be secure, blockchain technologies are not immune to vulnerabilities. Cryptojacking, where unauthorized mining occurs on personal devices, and smart contract flaws are examples of emerging risks.
- 5G Networks: The deployment of 5G networks promises faster connectivity but also introduces new security challenges. The increased number of connected devices and the complexity of the network architecture can lead to new entry points for malicious actors.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its nascent stages, quantum computing poses a significant risk to current encryption methods. The ability of quantum computers to crack complex cryptographic algorithms could render many security measures obsolete.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to develop and implement advanced security protocols that are adaptable and resilient. This includes enhancing encryption techniques, regularly updating security software, and fostering a culture of vigilance and continuous learning in the use of new technologies.
Effective Strategies for Cyber Defense
In this section, we delve into the robust methodologies and practices that fortify our digital environments against various forms of digital intrusion. The focus is on enhancing the resilience of our systems and data against potential breaches and unauthorized access.
Firstly, implementing a multi-layered protection approach is crucial. This involves the integration of various security measures at different levels of the system, from the hardware to the application layer. Each layer acts as a barrier, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to penetrate the entire system.
Regular software updates and patches are also essential. These updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious entities. Ensuring that all software, including operating systems and applications, is up-to-date significantly reduces the risk of exploitation.
Additionally, the use of robust authentication methods cannot be overstated. Implementing strong password policies and, where possible, multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. This makes it more challenging for unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive information or systems.
Educating users about the risks and best practices is another pivotal strategy. Often, human error is the weakest link in the security chain. Regular training sessions and awareness campaigns help users recognize and avoid common traps such as phishing attempts and suspicious downloads.
Lastly, continuous monitoring and incident response planning are critical. Having a proactive monitoring system in place can help detect and respond to anomalies in real-time. Coupled with a well-defined incident response plan, organizations can mitigate the impact of any security breach swiftly and effectively.
By adopting these strategies, entities can significantly enhance their defensive capabilities against the ever-evolving landscape of digital threats.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.
